Every time you notice an illuminating check engine light, it indicates that something is wrong with it. We tend to ignore this issue and treat it as unimportant, but delaying would lead to costly repairs. However, a qualified mechanic must be consulted as the Code won’t go away on its own. The illumination is generally followed by a code which is differs depending on the present car issue. Below is everything you should know regarding the car diagnostic code list, but before that, let’s look at the trouble codes divided into four categories as follows:
Powertrain Codes
These are the common form of codes, also known as P codes. It involves an engine, transmission, and emission systems. For instance, if you notice a P300 code, it is a random misfire code when a single or all the cylinders aren’t producing enough power as others. On the other hand, in the case it’s P303 Code, the power contributed by cylinder three is less than other cylinders present in the car. If you’re unable to know the cause of the problem, it’s time to check the Spark quality using a Spark tester. This tool is devised for different engine types, and instructions are written in simple language.
Body Codes
The next category of codes is the “B” codes, which generally include the climate control systems, lighting, and airbags system. Finding maintenance items for them is a hassle, so a qualified technician or sound technical and part knowledge is needed to resolve them. If the Code is associated with cabin filters and lighting items, ensure that you get the new ones from ‘The Auto Parts Shop‘ and fix them by yourself.
Chassis Code
Chassis code is, also known as C code, flashes only when there is an issue with the antilock brakes and electronic suspension and steering systems. The moment you start the car, you will see this diagnostic engine code flashing on your car. Sometimes the light comes on, and the wheels start locking up a faulty sensor, which is the underlying cause of the issue and must be taken to the mechanic for a diagnostic engine code fix.
Network Communication Codes
This is also known as “U” codes and involves controller area network wiring bus and modules. If your car has been flashing “U” codes for a long-time, the car must be taken to a qualified mechanic. Those with sound mechanical knowledge can read these codes using a car diagnostic OBD II code reader.
Vehicle Specific Codes/OBD II Codes
These are vehicle-specific codes if you ever come across the term OBD II codes. There is a distinct OBD Code for every issue, and a scan tool can help you determine the underlying cause behind the problem.
Top Check Engine Light Codes with their Solutions
You would come across several trouble codes, and it’s vital to determine the underlying reason as the check engine light flashes on the computer. Let’s know these diagnostic engine codes in detail and take measures to prevent them from popping again:
#1:P0300
Almost 18 Million scans were carried out in the year 2020 related to the P0300 Code. You would notice this Code when there is a misfire in one or more than one cylinder and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Check engine light flashing continuously.
- Engine moving roughly.
- Shortage of power
- Fuel smell coming from engine exhaust
- Hesitation or jerking taking place during acceleration
Causes
- Spark plugs have worn out
- Problems with spark plug wires or coils
- Distributor failure
Check your spark plugs, and in case their condition has got worse, a spark plug replacement would resolve the issues in no time.
#2:P0420 Code
Surprisingly,171182 vehicles with P0420 have been identified with these diagnostic engine codes. This Code appears only during a catalytic converter issue, and the vehicle starts releasing harmful pollutants from it:
Symptoms
- Illuminating check engine light
- Power shortage
- Reduced fuel economy
- Rotten egg or sulfur odor coming from the car
Causes
- Issues with an oxygen sensor
- Issues in the air-fuel Sensor
- Worn out or deteriorated CAT
- An exhaust system leak
- Misfiring
- Dense or lean air is to fuel ratio
- Gasoline filled with lead
Fixing P0420 Code will burn a hole in your pocket. Get top-quality car parts and accessories from ‘The Auto Parts Shop‘ at nominal rates and fix the trouble code yourself.
#3:P0171
Combustion engines maintain air is to fuel ratio with 14.7 parts of oxygen to one part of fuel. A P0171 means that the air is to fuel ratio has moved to bank one of the engine, and the air content in the mixture is in excess. Although the powertrain control modules do their best to add of adding more fuel to the engine, the ratios become so unbalanced that the P0171 starts flashing on the car again and again.
Symptoms
- Check Engine Light is on
- Lack of power from the engine
- Rough idle
- Engine coughing
- Engine misfiring
Causes
- Dirty or faulty MAF sensor
- Vacuum leaks in PCV hoses, vacuum hoses, intake manifold gasket.
- Weak fuel pump
- Clogged or dirty fuel injectors
- Clogged fuel filter
- Exhaust leak
- Faulty oxygen sensors
- Faulty air-fuel ratio sensor
An oxygen sensor replacement or fuel pump replacement would resolve issues taking place due to the P0171 Code.
#4:P0455
The moment the Engine control Module notices a big leak in the EVAP system. During this, the car starts releasing raw fuel and hazardous pollutants in the air that impact the environment and gas mileage.
Symptoms:
- Check engine light on.
- Reduced fuel economy
- Fuel smell
Most Common Causes:
- Missing, defective, damaged, or loose gas cap (Issue takes place often)
- Cracks in EVAP hose
#5:P0301
Misfires taking place in cylinder one often triggers the P0301 Code, and delaying it would prevent the engine from working completely. Take the car to the mechanic who would recommend appropriate diagnostic trouble code fix to you.
Symptoms:
- Check engine light is on or flashing
- Engine running rough and/or shaking
- Lack of power
- Fuel smell from the exhaust
- Hesitation or jerking during acceleration
Most Common Causes:
- Faulty or worn spark plugs
- Faulty spark plug wires or coils
- Distributor failure
- Faulty fuel injector
Take the car to a qualified mechanic for a diagnostic trouble code fix.
#6:P0456
This Code has been seen in the cars of 100,000 drivers and takes place when there is a leak in the EVAP system. The leak is small(less than .020″ in diameter), so there is no need to worry about it.
Symptoms:
- Check engine light is on
- Decreased fuel economy
- Increased vehicle emissions
- Fuel smell
Most Common Causes:
- Loose or damaged gas cap
- Leaking or disconnected EVAP hose
- Faulty purge volume control valve
- Faulty canister vent control valve
- Charcoal canister leak
- Leaking fuel tank
#7:P0303
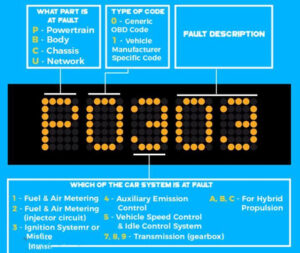
Code P0303 indicates that a misfire has been detected in Cylinder 3. 99,372 FIXD customers experienced this Code in 2020.
Symptoms:
- Check Engine Light is on
- Check Engine Light flashing
- Engine runs rough and shaking
- Lack of power from the engine
- Fuel smell from the exhaust
- Hesitations/Jerking when accelerating
Most Common Causes:
- Faulty or worn spark plugs
- Faulty spark plug wires or coils
- Distributor failure
#8:P0304
If a misfire is detected in Cylinder 4 of the car, it must be taken seriously as it would prevent the complete working of the engine.
Symptoms:
- Check Engine Light is on
- Check Engine Light flashing
- The engine runs rough and starts shaking
- Lack of power in the engine
- Fuel smell coming from the exhaust
- Hesitations/Jerkking as the car accelerates
Causes:
- Faulty or worn spark plugs
- Faulty spark plug wires or coils
- Distributor failure
#9:P0302
If a misfire has been detected specifically in Cylinder #2 of your engine, you see a P0302 Code. Neglecting it would have serious implications on the engine.
Symptoms:
- Check Engine Light is on
- Check Engine Light flashing
- Engine runs rough and shaking
- Lack of power from the engine
- Fuel smell from the exhaust
- Hesitations/Jerking when accelerating
Most Common Causes:
- Faulty or worn spark plugs
- Faulty spark plug wires or coils
- Distributor failure
#10:P0442
Whenever there is a medium-sized leak(.020″ to .040) in the car, it prevents the EVAP system from doing its job. It will be faced by 94,000 passengers in 2020.
Symptoms:
- Check Engine Light on
- Minimized fuel economy
- Surged vehicle emissions
- The smell coming from the fuel
Common Causes:
- Loose or damaged gas cap
- Leaking or disconnected EVAP hose
- Faulty purge volume control valve
- Faulty canister vent control valve
- Charcoal canister leak
- Leaking fuel tank
#11:P0128
The moment the engine starts getting hot quickly, the car starts popping P0128 Code. It starts impacting the emissions and fuel efficiency and must be resolved as soon as possible.
Symptoms:
- Operating Check Engine Light
- Higher than normal idle
- Decreased fuel economy
- The temperature gauge is unusually low
Most Common Causes:
- Stuck open thermostat (most common)
- Missing Thermostat
- Faulty coolant temperature sensor
- Faulty wiring for coolant temperature circuit
#12:P0446
Sometimes the fuel vapors move to the atmosphere, thereby causing vehicular pollution. This issue is generally taken care of by the EVAP system of the car. An electrical issue impedes the working of the EVAP vent.
Symptoms:
- Check Engine Light is on
- A slight decrease in fuel economy
- Gasoline smell
Most Common Causes:
- Missing, defective, damaged, or loose gas cap (most common)
- Defective EVAP Canister Vent Control Valve
- Distorted, damaged, or cracked Fuel Tank Filler Neck
- Torn or punctured Evaporative system hose(s)
- Defective Fuel Tank Sending Unit gasket or seal
- Split or damaged Carbon Canister
- Defective or damaged fuel tank
- Open or shorted electrical connections
#13:P0102
When you notice a low voltage output from a mass airflow sensor, your dashboard will start flashing the P0102 Code. You won’t experience any issues while driving, but it would negatively impact your fuel mileage.
Symptoms
- Illuminating check engine light
- Less power in the engine
- Reduced fuel consumption resulting in engine issues.
Causes
- Accumulation of dirt in the filter
- Problematic MAF sensor
- MAF sensors corroded or damaged
- MAF sensor screens covered with carbons
The only way to eradicate is via a thorough inspection of the air filter. In case the air filter condition isn’t up to the mark, an air filter replacement would resolve the issues in no time.
#14:P0113
Excess spark or fuel getting inside the engine impacts the air-fuel ratio, engine timing, and emission control, thereby leading to the P0113 Code.
Symptoms:
- Check Engine Light
- Trouble starting the engine
- The engine works in a lean manner
Most Common Causes:
- Faulty/Loose IAT sensor
- Faulty/Loose wiring connections
#15:P0441
Car’s EVAP system prevents the evaporation of raw fuel from the fuel storage system. These vapors become a part of the combustion process again, and when this thing doesn’t happen, the P0441 Code is initiated.
Symptoms:
- Check Engine Light
- Rough Idle
- Erratic Idle
Most Common Causes:
- Faulty purge valve (solenoid)
- Damaged or cracked charcoal canister
- Loose, damaged or missing gas cap
- Damaged or loose EVAP hoses
#16:P1000
P1000 refers to manufacturer-controlled diagnostic trouble code (DTC), mostly seen in cars like Ford, Jaguar, and Mazda. In other terms, it could mean different things in different cars. It happens as the battery gets dead or the cars become devoid of gas.
Symptoms:
- Check engine light is on
Most Common Causes:
- Disconnected battery
- Powertrain Control Module disconnected
- Clearing engine codes
- New vehicle
Check the car for a dead battery and take it to an auto repair shop for a dead battery replacement.
#17:P0306
P0306 refers to the misfire that has been detected in Cylinder 6 of your engine. This happens when insufficient fuel is burning in the cylinder and should be addressed immediately to prevent engine damage.
Symptoms:
- Check Engine Light is on
- Check Engine Light flashing
- Engine runs rough and shaking
- Lack of power from the engine
- Fuel smell from the exhaust
- Hesitations/Jerking when accelerating
Most Common Causes:
- Faulty or worn spark plugs
- Faulty spark plug wires or coils
- Distributor failure
#18:P0305
In case there is a misfire detected in Cylinder 5 of your engine. This happens when insufficient fuel is burning in the cylinder and should be addressed immediately to prevent long-term engine damage.
Symptoms:
- Check Engine Light is on
- Check Engine Light flashing
- Engine runs rough and shaking
- Lack of power from the engine
- Fuel smell from the exhaust
- Hesitations/Jerking when accelerating
#19:P0430
Sometimes Catalytic convertor present at the Bank 2 engine doesn’t work as expected, leading to the P0430 Code. Again, it is the inability of the convertor to break down the toxic substances, and these things impact your lungs, fuel economy, and atmosphere.
Symptoms:
- Check Engine Light on
- Lack of power from the engine
- Decrease in fuel economy
- Rotten egg or a sulfur smell from the car
Most Common Causes:
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Faulty air-fuel Sensor
- Worn or internally failing catalytic converter (commonly occurring)
- Leaky exhaust system
- Misfire (the root cause of converter failure)
#20:P0174
Surprisingly, P0171 has been noticed by 78,000 drivers, which means Bank 2 of the engine emits too much air or inadequate fuel. Driving for too long or not finding the diagnostic trouble code fix leads to overheating and damages the internal engine.
Symptoms:
- Illuminating Check Engine Light
- Lack of power from the engine
- Rough idle
- Engine coughing
- Engine misfiring
Most Common Causes:
- Dirty or faulty mass airflow sensor
- Vacuum leaks – PCV hoses, vacuum hoses, intake manifold gasket
- Weak fuel pump
- Clogged or dirty fuel injectors
- Clogged fuel filter
- Exhaust leak
- Faulty O2 sensor
- Faulty air-fuel ratio sensor
The Bottom Line
Don’t ignore these diagnostic trouble codes, and taking the car for a mechanic inspection would help you find the problem.
