There are a few things that can go wrong in constant velocity (CV) axle assembly. Leaking grease and everyday wear can make its parts worse. How do you know if your CV assembly is failing? Below is a list of negative CV features and other important information.
How do you say if your CV axle is wrong?

Here are some of the features that can point to a bad CV shaft:
- Clicking a sound when you turn
Damages in a CV axle due to frequent use can make the joints lose. As the external joints are unstable, they may produce a distinct sound described by some people as a click or a pop. This sound is most noticeable when making sharp or fast curves while driving around corners.
You will hear a strange clicking sound on the vehicle’s side with the damaged CV shaft.
- Clunking sound when you slow down or accelerate
You may hear abnormalities or knocking sounds from the inner CV joint assembly when you slow down or speed up.
The sound may come from a completely different source, but hearing it should be a cause for concern.
- Grease exposed to the bottom of the vehicle
The CV boot is something that keeps CV joints lubricated to make them function correctly. It is made of high-quality rubber that does not break easily.
However, if the boot is damaged, the grease inside it will flatten on the vehicle’s bottom as the axle turns.
- Trembling while driving
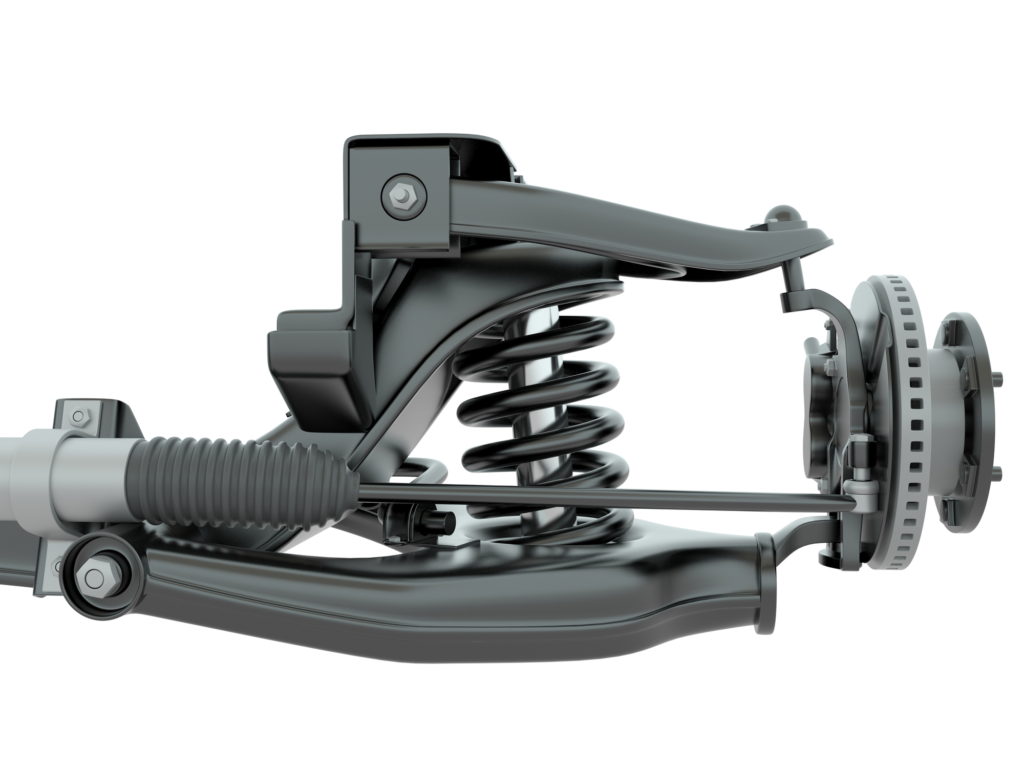

A damaged axle shaft or CV joint can affect the balance of the entire assembly as it rotates. When this happens, the shaft may move excessively. These vibrations can be intense as you accelerate.
Causes of failure in CV axle
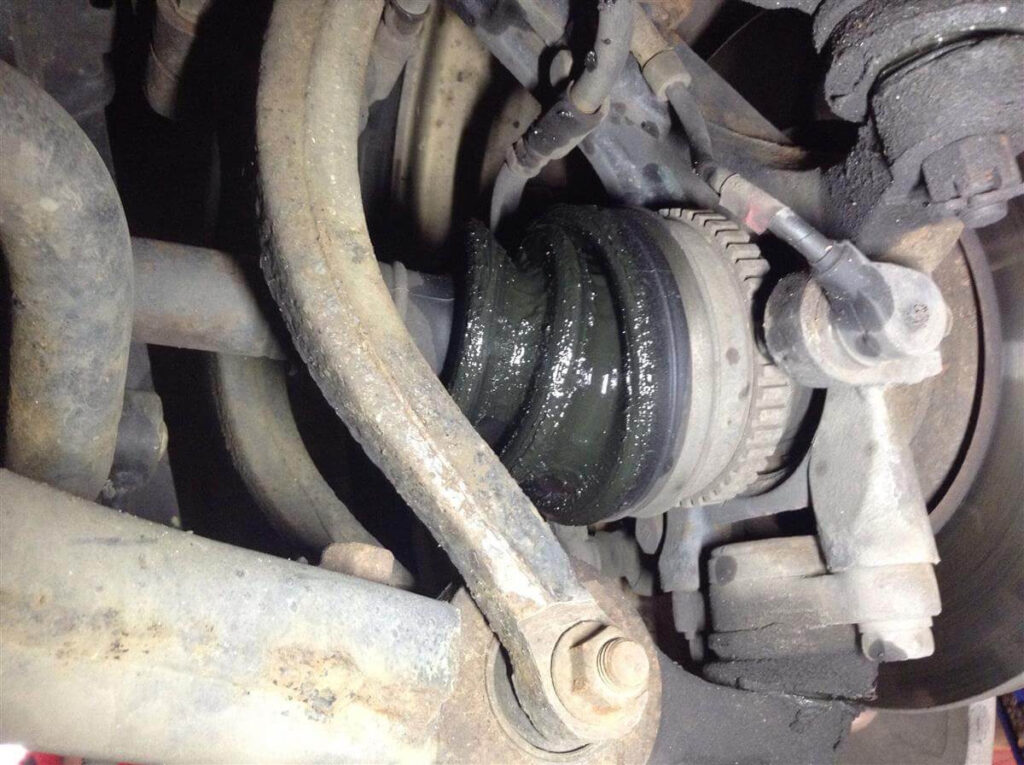

- CV axles and joints can wear out faster than usual if CV boot breaks or cracks. When this happens, the joints start losing grease and are no longer appropriately lubricated.
- Moisture, water, and other debris can get inside a broken boot, making CV joints more vulnerable to run out.
- Joints will fail even prematurely if they are set at an exaggerated angle due to the vehicle’s suspension.
- In some cases, CV joints may deteriorate over time.
How long can you spend on a bad CV?
If one of the CV axle joints fails, you may lose control of your vehicle. It can lead to horrible accidents that can cost lives, so always look for signs of the faulty CV axle and look at your car as soon as you see the red flags.
What is a CV Axle?
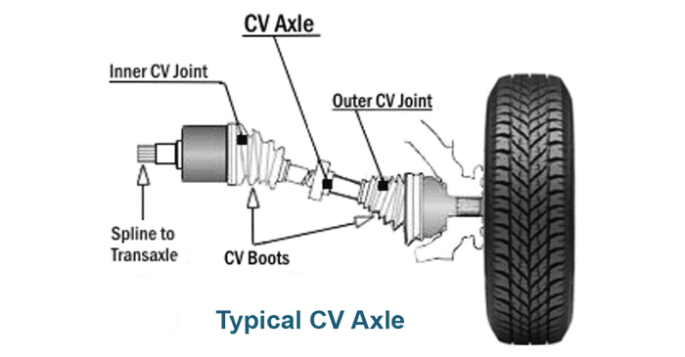
The CV axle (also called CV axle shaft and axle shaft) is responsible for moving the torque from the transaxle or difference to the wheels, enabling it to move forward. There are two CV mixers in its inner and outer ends that allow the CV shaft, which connects to the wheel hub, to transfer power without being affected by the different modes’ conditions. Oil-soaked rubber boots protect the joints.
Collectively, the shaft, the joints, and the boots make up an assembly of CV axles.
The CV axle is mainly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles to transfer engine power to two driving wheels.
Some of the later cars are equipped with an independent rear, and most four-wheel drive and all-wheel vehicles also have CV axles. The CV axle improves the quality of ride and vehicle capacity through these suspension systems, especially in off-road areas.
The function of vehicle CV axle
The CV axle is the drivetrain that transmits power from the transaxle or the difference to the steering wheels at a variable angle and the steady rotation speed without increasing the resistance. It facilitates the transfer of engine power to the wheels without affecting the wheel rotation.
The CV axle stretches from the vehicle’s transaxle or differential on one of the wheels. There are joints in both the inner and outer sides of the CV axle. These joints allow the axle shaft to move and change different road conditions without affecting the wheels’ transmission power.
In the absence of CV joints, axles can crack or bend whenever they are running on a bump or turning the corner. So you must check and maintain CV joints because it keeps the CV axle protected from powerful forces.
CV joints need to be lubricated regularly to function correctly, so there is a rubber boot to each joint. This rubber boot is filled with grease that helps the moving parts work correctly. The boot not only maintains lubrication on the joints but also protects the joints from dirt and debris.
If water or other road waste enters the CV joint, it will not be long before it is damaged. And when this happens, it will not be long before you start to notice signs such as strange sounds and vibrations, as described earlier.

Collectively, CV axels, joints, and boots serve as a system that ensures smooth and efficient mobility. You can buy them online at The Auto Parts Shop.
